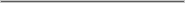A time when TVs were made of wood and children were not yet rabid.
A time when TVs were made of wood and children were not yet rabid.
In honor of Thanksgiving, a holiday which tends to emphasize family, I’ve dug up this AT&T Sceptre Videotext Terminal box art that I captured years ago. Look at those gloriously generic 1980s folks gathered around the TV set.
(I say “captured” for this image and not “scanned” because the image is actually a photo of the side of the box — the box itself is far too large to fit on a scanner. It’s roughly 14″ tall by 18″ wide by 11″ deep, if memory serves.)
Videotex: Smart TV in 1983
It’s funny: I’ve purposely avoided talking about Videotex on this blog for eight years because I was saving up material for a story about Teletext and Videotex. I have bought maybe a dozen vintage books on the two subjects since 2006 and mined news archives for information. But as they say, the best laid plans of mice and men oft go to Disneyland. Maybe I will get around to finishing that piece some day. Probably not.
So here’s the skinny. “Videotex” is the name for a graphical computer communications standard that was designed to display mixed visual and text information on regular TV sets. The idea was that a customer would buy a terminal (such as the one seen here), subscribe to a CompuServe/Prodigy/AOL-like online service, and use the terminal to connect to the service and view the information on their home TV set. Kinda like WebTV before the Web. Heck, kinda like smart TVs before the smart.
Graphically, Videotex used the NAPLPS protocol (similar to Prodigy, which grew out of these commercial Videotex experiments) to quickly transmit graphics to the user’s terminal. NAPLPS saves bandwidth because instead of storing/sending data on every pixel (like a bitmap image), the protocol describes graphics in terms of mathematical geometrical shapes (i.e. “draw a triangle at this location and fill it with orange,” like vector graphics).
By the mid-1980s, Videotex services fizzled in the marketplace. Their failure was likely due to low utility (not very useful), plus high cost of subscription (likely from high overhead on the service’s part in both hosting and creating content), and from competition from much more versatile and easier-to-interface-with personal computers.
AT&T Sceptre Videotex Terminal
And so that brings us to this side box art for a circa-1983 AT&T Sceptre Videotex Terminal. I bought this vintage gadget unopened, new-in-box on eBay for literally $1 plus shipping back in 2000.
The terminal works, but it has nothing meaningful to connect to — after all, the related Videotext service shut down almost 30 years ago. The last time I hooked it up, I believe I tricked its internal 300 baud modem to talk to my PC using a phone line simulator and perhaps even displayed a Linux console on the TV set. But that was many years ago. I also remember that the Sceptre has a horrible rubber IR keyboard that barely works.
One could conceivably create a Videotext simulator, hosted on a modern PC, that would pump NAPLPS graphics into to this vintage beast to bring it back to life. Maybe someone already has. If so, I’d like to know about it.
By the way, AT&T has a really neat vintage Sceptre promotional video on its website. It’s worth a watch.
[ From AT&T Sceptre Videotex Terminal product box, circa 1983 ]
Discussion Topic of the Week: Did your family ever subscribe to a non-ISP online service? Tell us about it.